Amazing Info About How To Lose Adipose Tissue
Lipodystrophy causes damage to adipose tissue, which prevents proper fat.
How to lose adipose tissue. Green says that stubborn fat deposits can accumulate throughout the body, but areas where stubborn fat deposits often collect include:. Brown adipose tissue is the major thermogenic organ in the body, and increasing brown fat thermogenesis and general energy expenditure is seen as one potential approach to treating obesity, added shamsi. Adipose tissue, otherwise known as fat, is generally found beneath the skin.
Written by nate furlong. What does brown fat do? The distribution of adipocyte diameter (d, in µm) in abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue before weight loss, at the end of weight loss, after 4 weeks of weight maintenance and after 9 months of.
Like the obesity epidemic, our understanding of adipocytes and adipose tissue is expanding. The best way to lose excess subcutaneous fat is with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Some subcutaneous fat is good for your body and helps protect it.
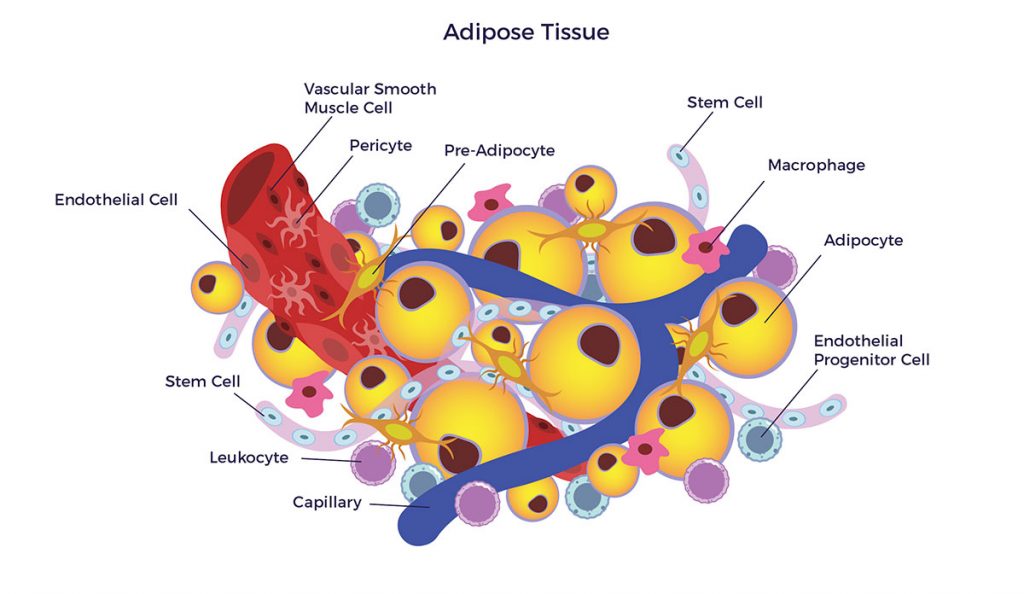
Each kind of fat serves a different purpose. Glossary all glands resources for glands. Based on the type of adipocytes, adipose tissue can be classified into two functionally different tissues:
Fortunately, there are a number of ways to lose excess belly fat, and in turn, reduce your risk of many health conditions. Adipose tissue (body fat) is how the body stores excess energy from food for use during times of scarcity. Hollywood's 퐄퐱퐨퐭퐢퐜 퐒퐞퐜퐫퐞퐭 for healthy weight loss.
It’s found just under your skin. The american journal of clinical nutrition: Excess adipose tissue can be found in people with obesity, which can be associated with adverse consequences for health.
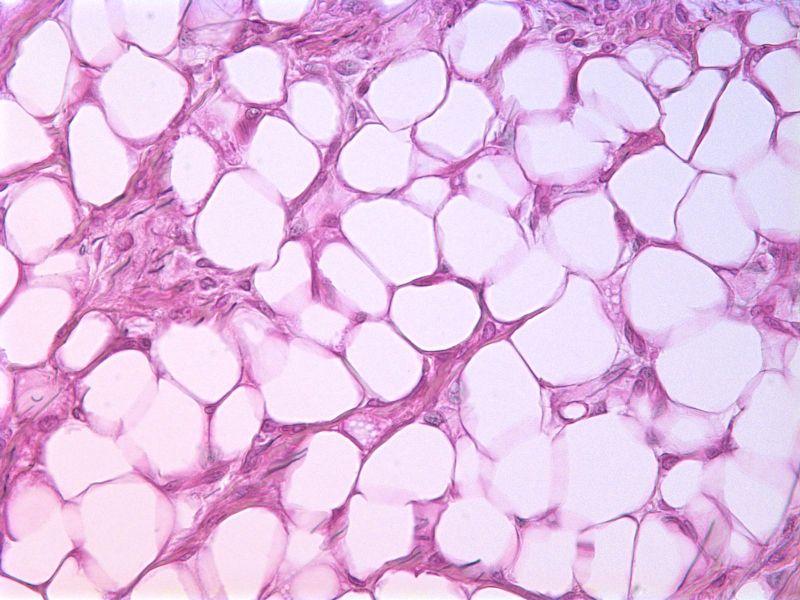
The effects of adipose tissue loss on your body. White adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. Subcutaneous fat is normally harmless and may even protect against.
Conversely, brown adipose tissue is protective against obesity. However, adipose tissue seems to have an obesogenic. How does adipose tissue collaborate with other organs?
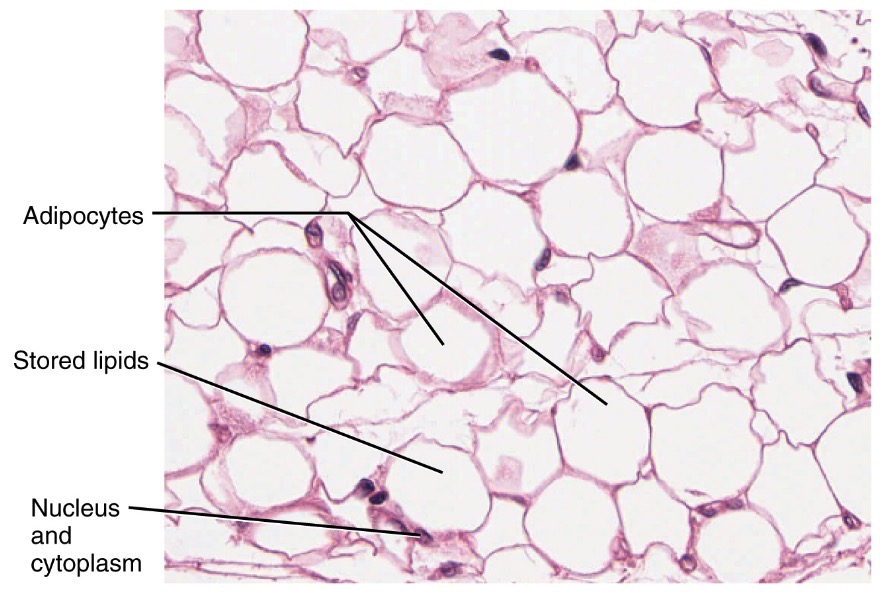
In the human body, there are two types of adipose, or fat, tissue: It produces heat by breaking down blood sugar (glucose) and molecules of fat. Weight loss would reduce the average size of resident adipocytes.
Upon weight loss, inflammation in the liver is resolved; Changes in the neuroendocrine inputs (sns tone and t3) that may be contributing to the adaptive response to weight loss are shown for each metabolic context. But too much body fat overall can lead to serious health issues including heart disease, diabetes, stroke and more.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adipose_tissue_2-5b48c694c9e77c0037187836.jpg)